Chapter 68: Influence of Muslim Thought on the West
Western Thinkers On Islam In General
Muslim philosophy influenced Western thought in several ways. It
(1) initiated in the West the humanistic movement;
(2) introduced the historical sciences and
(3) the scientific method;
(4) helped the Western scholastics in harmonizing philosophy with faith;
(5) stimulated Western mysticism;
(6) laid the foundations of Italian Renaissance and, to a degree, molded the modem European thought down to the time of Immanuel Kant, in certain directions even later.
1. The Muslims were the first humanists and they gave a humanist bend to the Western mind. They were the first to reveal to the West that outside the prevailing Catholic Church it was not all darkness and barbarism but untold wealth of knowledge. They captured and further developed all the intellectual achievements of Greece and transmitted them to the West before any direct contact between the Greek intellect and the Western mind was established.
It was through their influence that ancient and contemporary men outside the Christian West also began to be looked upon as human and even possessed of higher civilizations.
Nothing can prove their own humanism better than the fact that within eight years of the establishment of Baghdad they were in possession of the greater parts of the works of Aristotle (including the spurious Mineralogy, Mechanics, and Theology, the last of which was actually an abridged paraphrases of the last three books of Plotinus' Enneads), some of the works of Plato and the Neo-Platonists, the important works of Hippocrates, Galen, Euclid, Ptolemy, and subsequent writers and commentators, and several Persian and Indian writings on mathematics, astronomy, and ethics.
All this was taking place in the Muslim world when Greek thought was almost unknown in the West. While in the East “al-Rashid and al-Maman were delving into Greek and Persian philosophy their contemporaries in the West, Charlemagne and his lords, were reportedly dabbling in the art of writing their names.”
Humanism spread to Western Europe through contact between the Muslims and the non-Muslims in Spain; to Italy by a similar contact in Sicily; and throughout Europe by the impress of a higher culture received by the Crusaders in Syria and Asia Minor.
Since Islam originated from monotheism, it conceived idolatry as its real enemy and acted with the purpose of subduing it first in the Arab lands and then throughout the world. The Qur'an accepts Christianity and the Jewish religion as divine religions; therefore, it did not instigate any struggle against them. However, Christianity first conceived of Islam as a competitor and, therefore, attacked it directly.
The Arian and Nestorian sects of Christianity had a positive outlook on Islam since they were monotheistic in outlook. As compared to Islam the doctrine of the Trinity and the Monophysite mode of thinking retained the residues of idolatry. The places of ancient Jupiter, Apollo, Venus were given to God, Jesus, and Mary. Since iconoclasticism of Islam was against their frame of mind, the Christians started a religious struggle against Islam.
The following verses from the Qur'an indicate that in Islam there is no obligatory doctrination but religious tolerance: Lakum din-u-kum wa li-ya din (you have your religion and I have mine); la ikra'ha fi al-din (religion is not to be forced on anyone). On the other hand, the idea of proselytism is dominant in Christianity. Christianity indoctrinates that it is the only way to spread and spreading is its main duty.
In spite of this principle in Christianity, the spread of Islam in all domains from the first Hijrah on not by wars but sporadically was much more rapid. Barthold sees the reason for this in the capacity of the Arabic language and in the Islamic custom of not collecting taxes and duties from defeated nations if they accepted Islam.
Although these sociological factors play a significant role, the ease in accepting a natural and rational religion and its consistency with human idealism are additional reasons for the spread of Islam.
The Christian reaction to Islam in the East and West took different forms. Those who criticized the new religion vehemently and did not wish to accept it as a religion at all come first. John of Damascus in his book De Haeresibus, considered Islam to be heresy. The first Byzantine writer who referred to the Prophet was Theophanes the Confessor (202/817). He also attacked Islam as severely as John. Guilbert de Nogent's (518/1124) criticism was based on the fact that wine and pork were tabooed in Islam.
As an exception, Hilderbert de Lemans for the first time, in the Middle Ages in the West, stated that Muhammad was a real Prophet and he did produce miracles. Guillaume de Tripolis' work on Islam was written with extreme hate and was most offensive. Its descriptions were far from reality, being a mixture of mythical elements with history.
Peter de Cluny (d. 551/1156) translated the Qur'an into Latin for the first time. His work set the foundation for St. Thomas' attacks on Islam. Two helpers named Peter de Toledo and Peter Poitier participated in Peter Cluny's attempt at translating the Qur'an. The Latin translation of an epistle on the discussion over the principles of Christianity and Islam between 'Abd al-Masill al-Kindi who was the Caliph Mamun's secretary and Yahya al-Dimashgi was added at the end of this version of the Qur'an.
This epistle indicates how tolerant the 'Abbasid Caliph was about religious discussions even in the third/ninth century. When this work was translated into Latin in the West in the sixth/twelfth century, very bitter and offensive expressions were used for Islam in the preface to the Latin translation. Casanova and Muir critically investigated whether or not this epistle really belonged to the third/ninth century.
Massignon has looked for a relationship between the epistle of this al-Kindi-who has no relation to the philosopher al-Kindi-and that of Yahya ibn 'Adi in which the Trinity is defended.
The problem has not yet been solved.
St. Thomas referred to Islam and to its theologians. He is the first to give his criticisms a philosophical orientation. Raymond Lull (633-716/ 1235-1316) studied Arabic at Majorca and Muslim philosophy in Bugia near Tunisia. It was he who suggested to the then Pope to start the moral crusade against Islam.
This suggestion which was met at first with complete disinterestedness was later accepted by the Popes after Raymond's long endeavor to that effect; it became indeed the foundation of the Missionary movement. Raymond translated Asma' al-Husna (The Beautiful Names of God) of Muhyi al-Din ibn 'Arabi. He adapted several passages from Futahat al-Makkiyyah (The Revelations of Mecca).
He wrote an epistle relating to the discussions of a Christian, a Muslim, and a Jew. Although he wrote many epistles and books about Sufistic theology and philosophy, yet he essentially preserved his enmity against Islam.
At the same time Constantine Porphyrogenitus was referring to the Prophet with respect and politeness in a passage of his work on history. Ibn Sab'in, an adherent of tasawwu/, in qa book entitled al-Ajwibah 'an al-As'ila al-Saaliyyah (Answers to Sicilian Questions) answered the questions asked on Aristotle's philosophy by the King of Naples and Emperor of Germany.
Yet the moral tension between the two worlds did not ease. Dante in the section on “Inferno” of the Divine Comedy describes the Prophet in the eighth sphere of the underworld in a most atrocious manner, although, as Asin Palacios in his studies of his Divine Comedy demonstrates, he owed to ibn 'Arabi his entire topic, his manner of synthesis, and his idea of moral ascension. Since all the publications in the West against Islam for centuries after the Middle Ages had continuously been written by adaptations, translations, imitations, copying without any mention of source, they were no more than expressions of a complex against Islam as a faith.
It was at first rather difficult for the Western philosophers to get rid of religious, imperialistic, and racial prejudices and look at Islam and the East with understanding. In spite of the fact that Renaissance became possible only through profiting by Muslim works on philosophy, and science and their translations and interpretations thereof for centuries, the attitude of some Western people who were hostile to the very civilization that created these works indicates how deep-rooted the religious, political, and racial prejudices were.
From the eleventh/seventeenth century on, Western philosophers gradually got rid of their prejudices against Islam. Cultural and intellectual influences from the Muslim East for centuries were instrumental in bringing about that change.
From the twelfth/eighteenth century on, the attitude of Western free thinkers took a truly humanistic turn. The libre penseurs took a stand against negative and malicious publications. Edward Sale, in the preface he wrote for his translation of the Qur'an in 1147/1734, likens the Prophet to Thesee and Pompillus.
He praises his philosophy, his political views, and his realism. Boulainvilliers in his book, The Life of the Prophet, going one step further tried to prove that Islam is superior to Christianity in rationalism, realism, and its consistency with the nature of man. Savory in the preface he wrote for his translation of the Qur'an completed in 1198/1783, describes Muhammad as “one of the marvelous persons who appear in the world from time to time.” Due to its importance, Savory's translation was again published ten years ago.
This sympathetic attitude towards Islam evoked a strong reaction in Voltaire. He made extremely offensive and insolent statements about Islam and the Prophet of Islam. Kant praised Islam in his La Religion dans les limites de la simple raison. “Islam,” he said, “distinguishes itself with pride and courage, for it propagates faith not by miracles but by conquests, and it is founded on courageous asceticism.
This important phenomenon is due to the founder who propagated the conception of the unity of God. The nobility of a people who were freed from idolatry has been an important factor in bringing about this result. The spirit of Islam is indicated not in conformity without will but in voluntary adherence to the will of God, and this, above all, is a noble quality of a high order.”
In his Mahomet, Goethe, with great sympathy and enthusiasm, describes the power of the new faith exalted against idolatry, and the sincere adherence of its believers to it. This work of Goethe is in the nature of an answer to Voltaire's work bearing the same name.
Goethe read the Qur'an in 1184/ 1770 and annotated certain verses which were later referred to in Megerlin's German version of the Qur'an.
By this time the Prophet of Islam was well known in Germany as the founder of a “Natural Religion,” and a protagonist of intellectual advance. Megerlin's translation of the Qur'an (1186/1772) and that of Boysen's (1187/1773) were published in Germany in addition to Turpin's work, The Life of Muhammad, in which Muhammad is described as a “great Prophet,” “powerful mind,” “true believer,” and “the founder of natural religion.”
Auguste Comte, in his “Law of Three Stages of Social Development,” considers Islam to be the most advanced phase in his so-called theological stage and regards it even as preparatory to the metaphysical stage
Oswald Spengler compares Islam with the Protestant faith. In Muhammad he sees the puritan personality of a Luther or a Calvin. According to him, Islam calls for the same kind and quantity of “Illumination” and “Intellect” as was insisted on by Confucius, Buddha, Lessing, and Voltaire.
Although Nietzsche severely attacks Christianity in all his works, particularly in his Antichrist
he did not include Islam in his adverse judgment. On the other hand, he mentioned it with praise. Eduard von Hartmann, in his book entitled The Religion of the Future, remarks that, although Hebrew religion is an advance over paganism, the conception of monopolistic and rationalist God rather hinders its progress; and he concludes that monotheism finds it’s most powerful way of expression in Islam.
Carlyle designates Islam as a very superior faith and thinks that Muhammad is the hero of the prophets.
He refutes the false accusation made against the Prophet and states that “this kind of opinion is shame on us.”
Thus, Orientalism, interest in which began during the seventh/thirteenth century merely through religious fanaticism and with the aim at establishing missionary organization, gradually became a subject of methodical research.
After the twelfth/eighteenth century those who possessed intensive knowledge of Arabic began to occupy themselves with the study of Islamic sciences, principles of Islam, and the history of Muslim nations. The number of those who got rid of their prejudices and subjective views and who knew how to take truth seriously increased as scientific research became more extensive.
Dieterici, Sebillot, Quartermere, de Slane, Pococke, Sylvestre de Sacy, Fleisher, Wustenfeld, Horten, de Boer, Masson Oursel, Goichon, L. Gardet, Massignon, Rene Guenon, M. Asin Palacios, E. G. Browne, Nicholson, Sir Hamilton Gibb are among them. We may add that Orientalism today is oriented towards understanding Islam and other Eastern religions by serious scholarship, although there still are some who carry on their studies for imperial or missionary purposes.
In the above account an attempt has been made to show how, starting with thorough antagonism to Islam, the West gradually moved towards a humanistic approach to Islamic culture. But this humanistic attitude was directed not only towards Islam but also to other Eastern religions.
August Wilhelm Schlegel, from 1234/1818 to the time of his death, occupied himself with Oriental studies. From 1239/1823 to 1246/1830 he published the journal I ndische Bibliothek in three volumes and also edited the Bhagvad Gita and the Ramayana. These efforts mark the beginning of Sanskrit scholarship in Germany.
How the Jews and Christians in the West followed in the footsteps of Muslim thinkers in their recapture of Greek learning, and how they captured Muslim thought itself will be shown later.
2. A large part of the Qur'an refers to the past and takes the mind of the reader to the rise and fall of nations in the days gone by. In fact, it lays special emphasis on history as well as on nature as sources of knowledge. This Qur'anic attitude to history developed a true historical sense amongst the Muslims who in due course produced next to Herodotus world's first great historians like al-Tabari, al-Mas`udi, ibn Hayyan, ibn Khaldiin, and others.
One of them, al-Biruni, laid down for the first time in history the principles of historical criticism. The Muslims were, thus, the first after Herodotus to develop the historical sense and to lay open the various historical sciences before the West.
3. The greatest boon that the Muslim East bestowed upon the West was the scientific or inductive method of inquiry. Although most of the Muslim thinkers used the inductive method in their scientific investigation in different fields, the two of them who particularly expounded this method were Muhammad bin Zakariya al-Razi and ibn Haitham. Ibn Hazm, writing on the scope of logic, emphasized sense-perception as a source of knowledge. Later ibn Taimiyyah in his refutation of Aristotelian logic showed that induction was the only form of reliable inference. Suhrawardi Maqtul too offered a systematic refutation of Greek logic.
It was the method of observation and experiment which led al-Birimi to the discovery of reaction time, al-Kindi to the formula that sensation is a response of the organism proportionate to the stimulus, and ibn Haitham to his findings in optics.
The influence of Muslim method of observation and experiment on the West has been recognized by Briffault in the following terms. “Numerous Jews followed William of Normandy to England and enjoyed his protection establishing a school of science at Oxford; it was under their successors at that Oxford school that Roger Bacon learned Arabic and Arabic science.
Neither Roger Bacon nor his later namesake has any title to be credited with having introduced the experimental method. Roger Bacon was no more than one of the apostles of Muslim science and method to Christian Europe; and he never wearied of declaring that knowledge of Arabic and Arabic science was for his contemporaries the only way to true knowledge.
Discussions as to who was the originator of the experimental method…are part of the colossal misrepresentation of the origins of European civilization. The experimental method of the Arabs was by Bacon's time widespread and eagerly cultivated throughout Europe; it had been proclaimed by Adelhard of Bath, by Alexander of Neckam, by Vincent of Beauvais, by Arnold of Villeneuve, by Bernard Silvestris, who entitles his manual Experimentarius, by Thomas of Cantimpre, by Albertus Magnus.”
Science is the most momentous contribution of Arab civilization to the modern world, but its fruits were slow in ripening. Not until long after Moorish culture had sunk back into darkness did the giant to which it had given birth rose in its might. It was not science only which brought Europe back to life. Other and manifold influences from the civilization of Islam communicated its original glow to European life.
“Although there is not a single aspect of European growth in which the decisive influence of Islamic culture is not traceable, nowhere is it so clear and momentous as in the genesis of that power which constitutes the paramount distinctive force of the modern world, and the supreme source of its victory natural science and the scientific spirit.
“The debt of our science to that of the Arabs does not consist in startling discoveries of revolutionary theories; science owes a great deal more to Arab culture, it owes its existence. The ancient world was, as we saw, pre-scientific. The astronomy and mathematics of the Greeks were a foreign importation never thoroughly acclimatized in Greek culture. The Greeks systematized, generalized, and theorized, but the patient ways of investigation, the accumulation of positive knowledge, the minute methods of science, detailed and prolonged observation and experimental inquiry were altogether alien to the Greek temperament.
Only in Hellenistic Alexandria was any approach to scientific work conducted in the ancient classical world. What we call science arose in Europe as a result of a new spirit of inquiry, of new methods of investigation, of the methods of experiment, observation, and measurement, of the development of mathematics in a form unknown to the Greeks. That spirit and those methods were introduced into the European world by the Arabs.
4. In the West, even up to the ninth/fifteenth century, philosophy and science were regarded as antagonistic to religion. Hence the teachings of Aristotelianism and Averroism were banned, Bruno was burnt, Kepler was persecuted, and Galileo was forced to retract. Muslim thinkers, following Plato, Aristotle, and Plotinus, harmonized faith with reason and made possible, for themselves and for Europe, unhampered development of both.
5. European mysticism was also much influenced by the mysticism of Islam. Arthur J4 Arberry observes in The History of Sufism that “it is impossible, for example, to read the poems of the Spanish mystic St. John of the Cross without concluding that his entire process of thinking and imaginative apparatus owed much to those Muslim mystics who had also been natives of Spain.” In the beginning of the eighth/fourteenth century, Raymond Lull wrote on mysticism.
He was an accomplished scholar and founder of school of Oriental languages at Rome. His mystical writings are “beyond question” influenced by Sufi speculation. These are only a few examples of what Arberry regards as “unquestionably a general process.” In later times the influence of Persian mystical poetry on so great a genius as Goethe is too well known to be mentioned.
Miguel Asin Palacios, in his study of the influence of the Muslim conception of the next world on the Divine Comedy, investigated ibn 'Arabi's influence on Dante. The relationship between ascension to heaven in Dante's book and the Ascension (mi'raj) in Islam bad already caught the attention of some scholars. Ozanam, a thirteenth/nineteenth-century French scholar, in his great study of Dante, mocked at those who thought that the work of the poet from Toscana was “a lonely monument of the Middle Ages” and he considered the poet an erudite who was considerably well informed and who made use of all past experiences.
According to him, “two roads, one going north and the other south, lead Dante to the old Eastern sources. He maintained that the relationship between the Saracens and Europe was very close at that time.” Dante had read the Latin versions of the works of many Muslim philosophers and adherents of tasawwuf, at least those of ibn Sina and all-Ghazali.
Following Ozanam and d'Ancona, Charles Labitte, in the preface he wrote for Brizeux's translation of the Divine Comedy into French, maintained that the theme must have been borrowed from the world of Islam. At that time, Modi de Goeje and some other authors held similar views. More recently Edgard Blochet published two studies on this problem: Etudes sur l'mistoire Religieuse d' l'islam, 1307/1889, and Les Sources de la Divine Comedie, 1319/ 1901.
In these studies he defended the view that the idea of ascending to heaven came directly from Islam. According to Blochet, in a verse in the Qur'an, there is a reference to mi'raj (ascension to heaven) though no details are given. Many of these details are the products of public imagination in Islam and they must have been due to more ancient sources. He finds the roots especially in Mazdaism.
He relates the mi'rdj description in the Mazdakite poet Artay Viraf's literary work based on Zend-Avesta. Barthelemy translated Artay Viriif's Namak and in his foreword demonstrated similarities between the Divine Comedy and the Mazdakite book. Blocbet claimed that the idea of ascending to heaven in Dante was transmitted both from the Persian and Islamized sources.
Asin Palacios' conclusions are more precise. Not being satisfied with mere comparison between the texts, he studied the sources of Dante and thereby demonstrated how these depended on Islamic works, i. e., on their translations. By emphasizing the special significance of ibn 'Arabi's “Revelations”, he solved the problem with great success. Ibn Masarrah al-Jibali from Mercier and Cordova who specialized in ibn 'Arabi's doctrine of tasawwuf, demonstrated the influence of this doctrine on Western scholastics, in general, on the priests of the Franciscan denomination, and on Dante who was till then known as a follower of Aristotle and of St. Thomas in particular.
Palacios' book is composed of four parts: (1) comparison of the Divine Comedy with lailat al-isra and mi'rdj; (2) comparison of the Divine Comedy with Muslim descriptions of the next world ('uqba); (3) Islamic elements in the Christian legends before Dante; (4) studies and determination of the transmission of Islamic works to Christian Europe in general. In the first part, Asin studies the development of the idea of mi'raj in Islam. He traces this with reference to different texts and footnotes and compares each separately with the Divine Comedy. Many phantasies were created in the public imagination about a verse in the Qur'an on mi'raj.
All these got incorporated in the descriptions of descent to hell at night (isra) and the Ascension to heaven (mi'raj). The theme of mi'raj, which public imagination worked on, is used as a mystic symbol by ibn 'Arabi. Several adherents of tasawwuf, e.g., Junaid Baghdadi, Bayazid Bistami, etc. had used the moral symbol before. In ibn 'Arabi's work it received a more significant place. Later, in the books entitled Mi'raj Nameh and in Nizami Ganjeh's Makbzan al-Asrar the event of Ascension to heaven is related in great detail. Muslim miniature artists illustrated these works with many drawings about this spiritual journey.
The construction of Dante's hell is the same as that of ibn 'Arabi's hell. Both are large funnel-shaped edifices composed of several storeys. Spiral staircases lead down to these storeys, in each of which a different class of sinners is housed. The weight of the sinners increases as they descend further down. Each floor is sub-divided into various parts. The first floor in ibn 'Arabi's hell is an ocean of fire and corresponds to what Dante called Dite, on the shores of which there are various fire tombs.
Thieves, murderers, plunderers, despots, and the gluttons are tortured in the same chambers. The punishment of thirst given to the makers of false money in the Divine Comedy is given to drunkards in the Mi'raj Nameh.
The Prophet meets the angel placed at his service by God at the gate of heaven. He takes the Prophet to a group of nymphs in heaven surrounding the sweetheart of the poet Im u' al-Qais. In the same way, when Dante enters heaven, he meets a fair maiden Matilda who politely and elegantly answers his questions. The construction of heaven is the same in both images and is inspired by Ptolemy's Alma jest.
In accordance with the degree of their virtues, the happy souls are located in one of the nine heavens. Each of the nine heavens corresponds to a sign of the zodiac. Both works have a moral structure, assigning virtues to each storey or to each sphere in heaven. Islamic books entitled Mi'raj Nameh give the same amount of details and demonstrate the same kind of skill in the description of the heavenly world as is to be found in the Divine Comedy.
The eyes of both travelers are dazzled by getting near God as they enter a new phase of the mi'raj. When their respective guide Gabriel or Beatrice informs them of His grace, their eyes open. Gabriel and Beatrice not only serve them as guides, but also pray for them at each post. As finally Beatrice leaves her place to St. Bernard when Dante enters heaven, so does Gabriel leave the Prophet when he advances to the presence of God guided by a ray of light.
In studying Dante's Muslim sources, one has to compare the Divine Comedy with the Arab poet abu al-'Ala' al-Ma'arri's Risalat al-Ghufran. There is a close relationship between the religious ecstasy, charitable pity, and irony, orienting the feelings of the author of this book and the religious ecstasy, criticism, satire, and irony of Dante.
Since the topic of mi'raj is basic to the Arab poet's book too, in the absence of any historical documents to supplement a comparison of this kind, its study is still useful. In heaven, Dante meets his contemporaries Piccardo from Florence and Gunizza from Padua. According to abu al-'Ala', the Prophet meets Hamdum from Aleppo and Taufiq from Baghdad. Both have similar endings. As the Prophet in one case and Dante in the other enter the presence of God, they see Him as a strong ocean of Light.
The Muslim adherents of tasawwuf, with the exception of ibn Masarrah of Spain (270-319/883-931) and ibn 'Arabi, were not as well known in Europe as were the “philosophers.” Ibn Masarrah was the founder of the illuministic or Ishraqi School. From Spain the ideas of this school were transmitted to the Augustinian scholastics such as Duns Scotus, Roger Bacon, and Raymond Lull.
Yet Goethe wrote the Der west-ostliches Diwdn (Compendium of Poems on the East) during his mature years after reading Hafiz. Fitzgerald translated Kh-ayyam's Rubd'iyat into English and it was received with great interest. Nicholson published in several volumes English translation of Rumi's Mathnawi in addition to the selections from his Diwan and also from the Mathnawi.
Massignon has devoted his entire life to the study of Halaj Mansflr. The number of studies on the works of Harith Mulaasibi has increased recently. Aldous Huxley makes frequent references to Riimi in his Perennial Philosophy, and thinkers like Rene Guenon have been directly inspired by tasawwuf.
In our own times Corbin, by publishing the greater part of Suhrawardi Magtul's books in two volumes with their Arabic and Persian originals at Istanbul and Teheran entitled Opera Metaphysica et Mystica,
has brought the great martyr to the attention of existentialists and philosophical anthropologists.
6. The process by which Muslim thought laid the foundations of the Italian Renaissance and influenced subsequent thought was a long one. It will be briefly described in the sections that follow.
Theological Influence
The influence of Muslim theologians on the West was only secondary. Tension between the two religions, Islam and Christianity, was the reason for this. Nevertheless, Muslim theologians were known to the West even though indirectly through the works of the “philosophers”; only al-Ghazali`, theology was known to the Western scholars directly. St. Thomas refer to the theologians in his Contra Oenetiles as loquentes.
However, fm long knowledge of Muslim theology remained meagre and that for two reasons:
(i) the information about the Mu'tazilah and the first theologian was second-hand, nothing was taken from their own works; and
(ii) the masters of the philosophico-theological movements after al-Ghazali long remained unknown. Up to the thirteenth/nineteenth century hardly ani scholar in the West was acquainted with the works of Fakhr al-Din Razi
Saif al-Din 'Amidi, ibn Taimiyyah, Siraj &I-Din Urmawi, Sayyid Sharif al-Jurjani, Sa'd al-Din Taftazani, and others. No complete account can, therefore, be given of the influence of Muslim theology on the West.
However, important works on the philosophy of religion have been translated since the beginning of the present century. Among these the Irshad of abu alMa'ali (Imam al-Haramain) and several books by ibn Taimiyyah have been translated into French. In addition to these, Max Horten has published a big volume on Muslim theologians.
Recently, Louis Gardet together with Anawati has released Introduction a la Theologie Musulmane. Albert Nader has written Le systeme Philosophique des Mu'tazila (first published in Arabic and then translated into French by the same author).
Al-Ghazali had a unique position. He was a theologian as well as a philosopher. Therefore, his influence in the West was theological as well as philosophical. Miguel Asin Palacios studied al-Ghazali's theological influence on Western thought in several of his writings.
As it was previously assumed, this influence cannot be confined to the Tahafut only, the Latin version of which was made during the sixth/twelfth century. Al-Qhazali's influence was also effected through his other works.
The Magdsid was translated into Latin under the heading Logika et philosophea Algazelis Arabic by Gundisalvus; it was published in Venice in 912/1506. His al-Nafs al-Insdni was also translated under the title De Anima Humana. AI-Gazali's influence which Asin Palacios elaborately discussed in his book, La espiritualidad de Algazel su sentido cristiano, has several phases. The influence on Raymond Martini, a Dominican monk who profited by al-Ghazali's works on theology and philosophy, comes first.
According to Palacios, the influence of the early Christian sources, for instance of St. Augustine, on al-Ghazali himself should first be taken into consideration. Although it is not possible to indicate how and by what means Augustine's ideas were transmitted to al-Ghazali, it is quite possible that his influence was widespread in the intellectual circles where al-Ghazali was brought up.
Palacios, however, fails to refer to any evidence to prove his assertion, though he has much documentary evidence about the transmission of al-Ghazali's thought to the West. Take the case of historian-philosopher Bar Hebraeus known in the Muslim world as abu al-Faraj. He was a minister at a Syriac Jacobite church and was famous during the seventh/thirteenth century. He wrote in Arabic and Syriac and copied many chapters from al-Ghazali's Ihyd' (Revivification of Religious Sciences) and adapted them in his books entitled Ethicon and The Book of the Dove. This marks the beginning of al-Ghazali's influence on Christian spirituality.
If an author like Bar Hebraeus, who was rather influential in the Christian church, profits by al-Ghazali's ideas in writing his own books considered fundamental in monastery instruction, the reason for this, according to Palacios, was that he regarded these ideas totally consistent with his own doctrine.
In his study of al-Ghazali, Wensinck shows that the two books by Bar Hebraeus are not only written in accordance with the organization of the chapters taken from al-Ghazali's Ihya' (e.g., virtues, vices, the degrees of moral perfection) but also al-Ghazali's ideas and even his examples, analogies, and at times phrases, and the kind of evidence Ihya' brings from poetry and literature, are employed in them in exactly the same way.
According to Palaeios, Bar Hebraeus did so because in reality these were fully consistent with the Christian spirit even though he wanted to keep secret the apparent source of the ideas transmitted to him. However, there was no need for Palacios at this point to go into making interpretations which would contradict his own straight arguments.
Palacios traces the development of al-Ghazali s ideas in the West as follows. The Spanish Dominican monk Raymond Martini, who was Bar Hebraeus' contemporary, borrowed the same ideas from him and from al-Ghazali. Instead of profiting only by the books of Muslim “philosophers,” he, unlike the scholastics, directly profited by al-S;hazali's texts in his books entitled Pugio Fidei and Explanatio Symboli, written in the field of religion. These texts were taken from Ta/ed/ut, Magasid, al-Mungidh, Mizdn, Magsad, Mishkat al-Anwdr and Ihyd'. According to Palacios, the benefit derived here is more substantial than Bar Hebraeus' adaptations which he had made without mentioning any source, for the arguments have been taken exactly as they were in the original.
Furthermore, St. Thomas used some texts of al- 'hazali's in Contra Gentiles either directly or through the mediation of Raymond Martini. Al-Ghazali's arguments in favour of the creatio ex nihilo, his proof that God's knowledge comprises particulars, and his justification of the resurrection of the dead were adopted by many scholastics including St. Thomas. St. Thomas, who had received his education from the Dominican order in the University of Naples, had known al-Ghazali's philosophy well, and used his arguments in attacks on Aristotelianism.
St. Thomas' Summa Theologica and al-Ghazali's treatise on the place of reason as applied to revelation and theology run parallel in many places in their arguments and conclusions. Both of them claimed to have found happiness in the beatific vision and both stated the case of their opponents fairly before pronouncing their own judgments on it. The questions on which St. Thomas seems to have been deeply influenced by al-Ghazali are the ideas of contingency and necessity as proving the existence of God, divine knowledge, divine simplicity, divine names, and divine attributes, God's speech a iverbum mentis, the miracles as a testimony to the truth of prophecies, and resurrection of the dead.
Al-Ghazali's influence was very significant towards the end of the Middle Ages. During the eighth/fourteenth century, three sceptic philosophers were influenced by al-Ash'ari's arguments on the problem of causality through the mediation of al-Ghazali. Their names are (1) Peter of Ailly, (2) Nicholas of Autrecourt, and (3) Gillaume of Occam. Occam, the scholar most influenced by al-Ash`ari's nominalism in the West, arrived at the conception of intuitive divine knowledge via his own criticisms of the theory of causality and his occasionalism (by which he tried to explode St. Thomas' rationalistic philosophy) under al-Ghazali's influence.
A relation was established for the first time between Christian and Muslim philosophies with Gundisalvus' translations from al-Ghazali. C. Baumker was the first to call public attention to these translations. From the works of this great scholar (as later from those of E. Gilson) it has become clear that ibn Sina had an influence on the West in two ways: (1) directly through his own works and (2) indirectly through al-Ghazali's works translated by Gundisalvus.
Al-Ghazali was in a way ibn Sind's disciple even though he later opposed him. First he elaborated the ideas inspired by him, and later he criticized them. For instance, he followed the philosopher's point of view in the classification of souls. Ibn Sins, divided the soul into three faculties named in Latin: vegetabilis, sensibilis, rationalis. In al-Ghzali's translations, the terms used are: anima vegetative, anima animalis, anima humana (al-nafs al-nabdti, al-nafs al-hayawdni, al-nafs al-insdni). As to nafs al-ndtigah (the soul endowed with the gift of speech) Gundisalvus uses slightly different terminology. Above the hierarchy of the intellects there is al-'aql al- f a”dl (intellectus agens) which al-Ghazali designates as Substantia existens per se quae non est corpussubstance existing in its own right without the need of body-a definition which we do not find in ibn Sina and which proved valuable for the Western scholastics. Al-Ghazali calls the active intellect dator formarum.
Al-Ghazali's influence on the West was not confined to Raymond Martini. In his book Huellas des Islam, Palacios carries this influence down to Pascal. According to him, there is a conformity between al-Ghazali's and Pascal's ideas about the next world which is not due to coincidence. The sort of argument concerning the defence of religion extensively employed by al-Ghazali, known in the West as “betting” (pari), is elaborated again and again by Pascal in his Pensdes. In addition to Lachelier's well-known study on this topic, the same theme has also been studied by E. Degas in his Pari de Pascal.
Statement of the argument aims at making the non-believers see that there is no inconsistency in performing religious duties and believing in the possibility that the next world may not exist at all. This argument may be summarized in one sentence: If you win you shall win all; if you lose you will loose nothing (Si vows gagnez zoos gagnez tout, so vows perdez, vans ne perdez rien). Those investigating the roots of this argument give us information about a short text by Arnobiu who, after Bayle, was the first to use it. Another text in Sohund's Theologie Naturelle concerned itself with those roots. Finally, two French theologians, who were contemporaries of Pascal, formulated the betting argument in a way similar to his.
One of them was Silhon, the author of Immortalite de l'Ame. Blanchet and Lachelier studied in what ways these authors were like Pascal and how they differed. Following a penetrating analysis of the text, Blanchet demonstrates that they were Pascal's sources both in ideas and literary form. The result of these investigations is as follows. Pascal's betting idea was held by many authors in embryonic form since Arnobiu.
The idea took a long journey from al-Ghazali to Raymond Martini and then to Pascal. Let us see only the comparisons Palacios draws between Pascal and al-Ghazali basing them on well-founded studies of the texts. Pascal, like al-Ghazali, is of the opinion that our senses may deceive us. Here, Palacios compares the text of al-Mungidh with that of PensEce and indicates the similarities. Pascal as much as al-Ghazali strongly suspects that our dreams are the reality, our life is nothing but a dream when we are awake, and that we wake up from that dream when we die.
The resemblance to the effect that life is a dream and death waking up from that dream is significant. Both philosophers find the way to get rid of the state of doubt in mysticism. Both of them look for it in divine inspiration as a product of moral virtues and love of religion free from all logical judgments. This power of inspiration bestowed by God on the believers is the most dependable source for knowledge of the supernatural world, both in al-Ghazali and Pascal.
It is evident that the foundation of Pascal's theory about the “logic of the heart”
was laid in al-Ghazali's idea about the “eye of the heart.” Both assigned deductive intellect to the lowest category, for it has practically no influence on our emotional life and beliefs; the mental attitudes determined by it vary; its field of activity is confined to a limited number of elite; and most people remain outside its influence. On the other hand, the functioning field of practical life which is based on habits, familiarity, imitation, and the emotions of the heart is very broad and can be considered to be the common and normal foundation of religious life.
Palacios compares the ideas of al-Ghazali and Pascal on faith and human certitude, and also the anecdote on p. 68 in al- Ghazali's Faisal al-Tafriqah with that on p. 350 in Pascal's Pennies. In terms of ideas, both say the same thing, viz., “God is felt not in the intellect but in the heart” (Dieu est sensible au c.xur, non- a la raison). Then, Palacios notes the following points in Pascal about “betting” which remind us of al-Ghazali.
(i) The indifference of non-believers and free-thinkers towards the problem of the next world and eternity is stupid. It shows a weak intellect, an evil heart, and faulty perception. The Spanish author compares Pascal's work with al-Ghazali's Mizdn al-'Amal (Criterion of Action) and Ihya' in this respect. '
(ii) In order to remedy the indifference of this group of non-believers it is not sufficient to depend on objective arguments, intellect, and faith, for, the state of doubt they are in originates from the doubtfulness of the causes of existence and the non-existence of the next world. Therefore, one should begin with the hypothesis which would affirm the impossibility of definite arguments concerning the eternity of the soul. Here, Palacios compares Pascal's Pennies with certain chapters and passages in al-Srhazali's works, e.g., Ih,d', Mizan, and Arba`in, and shows how the arguments in them are repeated by Silhon and Pascal with very little change.
(iii) If one begins with the above hypothesis, in case of the insufficiency of convincing arguments by direct proof, one should look for such an argument as would recommend the idea of the existence of the next world where rewards and punishments should be calculated after death, depending upon personal interest, egotism, and the rules of most elementary caution and thereby convince non-believers of it. Here again Palacios compares passages from alghazali's works, e.g., Ihya', Mizan, Arba'in, Mustazhiri, with the texts of Silhon, Sirmond, and Pascal.
(iv) Above all this argument consists in putting the problem of next life in the same way as the possibility of success in present life in terms of the game of chance and fate. The game of fate consists of actions and events dependent on chance, like hunting, taking a sea-trip, wars, surgical operations, drugs for therapy, commercial transactions, professional education, new industrial enterprises, etc. The person who takes measures in all these activities calculates that the gain which is expected to be obtained in the future would be more beneficial than the one that is risked. Here Palacios points out that in his Ihya' and Mizan, al-Ghazali used the examples of hunting, commerce, political occupation, taking a sea-trip, drugs, and industry, and that as a matter of fact Pascal repeated many of them.
(v) The bulk of the argument is like the process of weighing as in a pair of scales. The values of the gains risked by betting as to whether the next world existed or not were put on one tray of this pair of scales and the values of the gains and losses, in either world, were put on the other. Here, Palacios gives examples from al-Ghazali's books, e.g., lhya', Mizdn, and Musta.Ihiri, and compares them with those in the works of Silhon, Sirmond, and Pascal. Pascal says, Lequel prenez vows voyonn; pesons le gain et la perte.
(vi) The first point to be taken into consideration in order to complete this comparison is that the pleasures and properties of this world should be weighed and then their uselessness and total quality stressed. The limited use that can be made of one's worldly possessions, during the lifespan lasting for about seventy years, should be emphasized. Texts from al-Ghazali's Ihya', Mizdn, and Muatazhiri are compared here with those of Sirmond's and Pascal's.
(vii) The eternity of next life (the loss or gain of which is the case in point), i.e., its infinity, limitlessness, unique timelessness which cannot be compared with millions of years and centuries, is weighed. For this too Palacios makes detailed comparisons between al-Qhazali's and Pascal's texts.
(viii) It is understood that there is no comparison between that which has an end and is limited and that which is unlimited and is endless, in terms of the worth and quality of values. The party that wins is of those who choose the road of virtue and accept the existence of the next world, thus getting rid of the sinful pleasures of this life. Here, Palacios compares parts of Mizan, Ihyd', and Arba'in with the like parts in the works of Pascal. “The one who does not believe is the loser.”
(ix) This argument may leave the possibility to the infidels of raising the objection that it is based on doubt about the things to be gained or lost in the next world. We have no definite idea about a thing to be gained or lost in the next world, whereas in this world we can determine with absolute certainty the things we are going to gain or lose. There is doubt about the matters of the next world but definiteness about those of this world.
(x) This difficulty is solved by pointing out that a limited thing which is definitely risked is negligible as compared with the infinity of expected gains even though doubtful. Here too Palacios makes comparisons between the texts of Mizdn al-'Amal and Ihya' and those of the works of Sirmond and Pascal, and indicates striking similarities between them.
(xi) Finally, assuming that the next world does not exist, if the laique person who is not under religious discipline acts virtuously in this world, he shall lose nothing. For the real happiness that man can find on this earth is not merely the satisfaction of his passions. Just the opposite; it comes from controlling the passions, putting them under the control of the intellect. Only in that way can man rise above the level of animals.
This state saves man from becoming a slave to sensuality and helps him gain his true freedom which gives him nobility. It enables him to get rid of anxiety, sorrow, mental weakness, and leaves him with infinite peacefulness of the soul, which is purer and more lasting than the sensuous pleasures. Here also Palacios quotes from Mizdn al-'Amal, Arba'in, Mustazhiri and shows how many of Pascal's statements resemble those of al- Ghaziili.
According to Palacios, it should be granted that there are some differences between the two# philosophers besides their similarities. First of all, like Sirmond, Pascal did not present the problem openly but mentioned it in an indirect way. Al-Ghazali, however, made a careful and detailed study of it. The point mentioned in paragraph (xi) illustrates this. According to Palacios, neither Sirmond nor Pascal stated the problem as thoroughly and analytically as al-Ghhazali did.
Thus, if the irreligious people and free-thinkers act virtuously, as if the next world really did exist, they will strengthen their position when a world which is doubtful for -them materializes in the future. Besides, they would be acting in a way which is consistent with their interests in this world. The direct source for the betting problem lies in self-interest and the principle of expediency.
This kind of reasoning directed against the irreligious and the free-thinkers who disregard all metaphysics and altruism is consistent with the rule of argument ad hominem which consists of using the arguments of the opponent against himself leaving him no way of escape. “If you win, you win all; if you lose, you lose nothing” principle will constitute the strongest proof for them. However, so long as they are convinced that as they bet in favor of the existence of the next world, which establishes control over their appetites, not only is earthly happiness which is very dear to them not sacrificed, but is, on the other hand, realized positively and fully.
Al-Ghazali explains the critical aspect of the betting idea better than Sirmond and Pascal. For neither of the two thinkers debates with the irreligious who directly refute the next world and consider the religious dogma a mere fake and absolute nonsense. Sirmond and Pascal argue only with those who are in a state of hesitation because of the lack of positive arguments to reach a decision. Al-Ghazali begins debating with the irreligious in Ihya' 'Uliem al-Din because of their ruthless actions and in Mizdn al-'Amal and Arba'In he faces them and meets them on their own ground.
In doing so, al-Ghazali's aim is to make them believe that they will find the positive happiness of the only life they believe in and wish to lead, not in loose life but in knowledge and virtue. According to Palacios, al-Ehseems more open and thorough than Pascal on betting. Pascal's Pensdes does not seem to be a completed work as al-Ghazali's books are. It is in the nature of an outline which the philosopher intended to develop in a complete work. His death, however, hindered that plan. But the mathematical clarity of Pascal and the results of his calculations of probability cannot be found in al-Ghazali. Palacios finds the reason for this in the Muslim philosopher's Islamic view of regarding all chance games as illegitimate.
Philosophical Influence Before Descartes
Interest in Muslim philosophy developed in Europe towards the end of the fifth/eleventh century. The Muslim rule in Spain, the Crusades, the seminaries in Sicily, the inadequacy of the old Western scholastic and scientific systems, and the density of population and internal congestion necessitated relations of the West with the world of Islam. In Toledo Muslims and Christians lived side by side. It was here that Raymond I, Archbishop of the provincial capital (525/1130-545/1150), established a translation bureau to render Arabic masterpieces into Latin.
In France and especially in Normandy, scientific trend appeared first among the monks. Robert, the King of France of the Capetian dynasty, at one time a disciple of Gilbert's, was friendly towards the Muslim scientific endeavor. At the time he invaded southern Italy, Calabria, and Sicily, he observed the Italian seminaries and borrowed many things from them. In that way, the seminaries of Sicily and Naples acted as transmission media of Islamic science to the West.
The transmission of Muslim thought to the medieval West passed through the following phases.
1. In the first phase, a band of scholars went to Muslim countries and made personal studies. Constantine of Africa and Adelhard made studies of this sort for the first time. Constantine, who was born in Carthage near the end of the fifth/eleventh century, travelled all through the East. He made translations into Latin from the Arabic translations of Hippocrates' and Galen's books in addition to those of the original works of Muslim scholars on medical science.
Later on, many students from Italy, Spain, and southern France attended Muslim seminaries in order to study mathematics, philosophy, medicine, cosmography, and other subjects, and in due course became candidates for professorship in the first Western universities to be established after the pattern of the Muslim seminaries.
2. The second phase starts with the founding of the first Western universities. The style of architecture of these universities, their curricula, and their method of instruction were exactly like those in the seminaries. First, the Salerno seminary was founded in the kingdom of Naples. Courses were offered in grammar, rhetoric, logic, arithmetic, music, geometry, and cosmography. Books of Aristotle and those on the interpretation of his philosophy were brought to Italy by way of Salerno.
Emperor Frederick of Sicily was known as a patron of Muslim science. He founded the seminary at Naples. Aristotle's books were translated from Arabic into Latin by his order. He corresponded with ibn Sab'in on philosophical matters.
Alphonso X, King of Castile and Leon (650/1252-683/1284), ordered that astronomical tables be made following a study of Arabic works. At that time, important seminaries were also established at Padua, Toulouse, and later at Leon.
3. At last, the science of the Musalmans was transmitted to France and to other Western countries via Italy. Bologna and Montpellier seminaries were founded at the beginning of the seventh/thirteenth century. The University of Paris opened its doors for instruction somewhat later. At that time Oxford and Koln Universities were established after the same pattern and thus the new science was transmitted to England and Germany.
During the seventh/thirteenth century, the Oxford school became a centre of the activities of translation and interpretation. Here for the first time Alexander Neckam translated from Arabic Aristotle's books “On Heaven” and “On Soul.” In the same School Michael Scot translated into Latin a book by al-Bitraji (Albatragius) on cosmography and several books by ibn Sina and ibn Rushd. Robert Grosseteste was another member of the Oxford Group (651/1253).
His efforts were noted in the translations of Greek and Muslim philosophical works. Roger Bacon (611/1214-692/1292) was the most important member of this group. This great scholar who made researches in language, mathematics, and biology became known as a magician and occultist during the Middle Ages and was, therefore, convicted; in fact he was one of the founders of empiricism. The influence of Muslim philosophers on Roger Bacon, particularly that of ibn Sina, was very great.
The word “experiment” (experimentum) is closely associated with his scientific and extra-scientific studies. While the trends initiated by ibn Sina and ibn Rushd constituted the roots of Western rationalism, Muslim naturalists like al-Razi and ibn Haitham influenced the empirical thought of England.
The best known Polish author during the translation period was St. Thomas' friend Wittelo (b. 628/1230). Wittelo went from Poland to Italy. He compiled an important work about Greek and Muslim scholars. In his book entitled Perspective, there were important selections from Euclid, Appolonius, Ptolemy's Optica, and ibn Haitham's Kitab al Manazir. Wittelo and Roger Bacon carried further ibn Haitham's work in physical research.
In the University of Paris, from the day it was established in 612/1215, much importance was given to Aristotle's texts and their interpretations in Arabic. From 629/1231 on, the Pope Gregory IX renewed the decree against the instruction of Aristotle and his texts. In the following years the Pope's actions against the universities became increasingly severe. Bacon, Duns Scotus, and Nicholas of Autrecourt were convicted. Investigations were made about the Averroists; they were convicted and circulation of their books was prohibited. These severe actions continued until the end of the eighth/fourteenth century.
These severe measures which had originated from fanaticism had ideological roots too. In general, they embodied a reaction against Aristotelianism. The tendency of Platonism and dialecticism against Aristotelianism and experimentationism was again aroused. Muslim philosophy was unable to meet the needs of the West when it came to Plato's Dialogues. For, many of them were not known to the Muslims. Those that were known were incomplete.
At the end of the ninth/fifteenth century extensive publication of books translated into Latin from Arabic rendered the decrees by the priests partially ineffective and these books rapidly spread everywhere, even outside the university curricula; while the mental orientation towards experimentation was now struggling against reaction in the fields of ideology and research, the ground was being laid for the Renaissance.
The translation into Latin of the works of abu Bakr Zakariya al-Razi, founder of the philosophy of nature in Islam, was an important step in the transmission of Muslim philosophy to the West.
Constantine the African translated into Latin two philosophical works of al-Rfzi, Kitab al-'Ilal and Sirr al-Asrdr, and Gerard of Cremona translated al-Mansuri, another work of his, under the title Liber Albubatri Basis qui dicitur Almansoriua. Al-Razi's greatest work Kitab al-Hawi (Liber de Continens) was translated into Latin and the Latin translation was published several times.
It was translated by Faraj ben Salim known as Faragut, a Jew educated at Salerno, in twentyfive volumes, under the orders of the King of Naples. It was first published in 892/1486 in Brecia, then in Venice in 906/1500, 912/1506, 915/1509, and 949/ 1542. Al-Razi's influence was not confined to the Latin translation of his works only; it led further to the translations of other Muslim philosophers who referred to him in their works.
The famous Jabir bin Hayyan is known among the naturalists as an alchemist, chemist and philosopher.
He is known in the Latin world better than in Islam, not as a philosopher and chemist but as a magician and alchemist. Summa pert ectionis magisteri is a translation of his collected works.
E. Gilson, in a number of detailed studies, investigated how Aristotle's psychology reached al-Farabi and al-Kindi, how it developed in their hands, and how it was transmitted to the Latin world.
Many of al-Kindi's books were translated into Latin. Plato of Tivoli translated his book on the problems of geometry; Arnold of Villanova, his books on degrees under the title De Gradibus; Robert the Englishman, his book on astronomy entitled “On the Dragon”; and de Azogont, his book on physics and meteorology.
This last book was first printed in Venice in 913/1507 and then in Paris in 947/1540.
One of al-Kindi's important books, Kitab al-'Aql (Book of the Intellect), was translated into Latin perhaps by John of Seville under the title De Intellectu. Gerard of Cremona also translated some books by the philosopher. According to Quadri, Giordano Bruno, the great philosopher of the Renaissance, refers to al-Kindi thus: “Al-Kindi is an Arab philosopher. Among the first scholars he is the best. Ibn Rushd profited by his books. Does this not signify his power?”
In the West, al-Kindi was known as one of Aristotle's faithful disciples and, therefore, for a long time, was considered to be a heretic. However, with his works and those of his successors, empiricism penetrated into the West from the Arab world and helped the rise of modern thought. Quadri notes that besides al-Kindi's book “On the Intellect,” the Latin translation of two other works of his, namely, Liber de quinque essentiis and Liber introctorius in artem logica demonstrationis, were also known in the West.
The latter was compiled by his disciple Mubammad ibn Taiyib al-Sarak-hsi; its authenticity, however, is doubtful. The former marks progress in the classification of the intellects and is a very important work. According to Latin texts, al-Kindi's philosophy is inclined towards Neo-Platonism.
Coming to al-Farabi, not all but some of his works were known in the West during the Latin medieval period.
Translations were made into Latin from his psychology, metaphysics, and logic. Through these translations he had a penetrating influence on Latin philosophers of the medieval West.
One of the most important figures in the translation activity during the Western Middle Ages was Gundisalvus (d. 546/1151). He was the spiritual leader at Segovia; in addition to numerous translations, he wrote a book, De Division Philosophiae, which imitated al-Fhrabi almost step by step.
In this book he substituted al-Farhbi's encyclopedic classification for the system of seven types of knowledge (trivium et quadrivium) which was traditional in the East during the medieval period,
and this classification which was very new and original for the Western world was followed for long in the then recently established universities.
Gundisalvus' translations had an influence on Christian scholastic philosophy, newly awakened during the seventh/thirteenth century, and especially on St. Thomas and Albert the Great. Al-Fiirabi and, following him, ibn Sina added the third form of the famous cosmological proof of God based on the conceptions of possibility and necessity, the first two being based on the ideas of motion and potentiality as formulated by Aristotle.
It was taken up from ibn Sina by the Jewish philosopher, Maimonides, and from him by St. Thomas Aquinas, and then it passed on to Spinoza and Leibniz. It was this proof that Kant criticized as the model cosmological proof. Al-Farabi's idealistic logic, according to B. Carra de Vaux, produced a permanent effect on the logical thought of Latin scholars.
Robert Hammond, comparing the arguments of St. Thomas about the existence of God with al-Fhrabi's, has recently shown his influence on the Christian philosopher.
By placing some other ideas of these two thinkers in opposite columns as follows, Hammond reinforces his views regarding this influence:
The proof of movement:
The proof of movement:
Due to our sense it is evident that in this world there are things that move. Each being is moved by something else. Summa In this world there are moving beings. Each being is moved by aninstigator.'Uyutn al-Masa'il
Active cause:
Al-'illat al-fa'ilah:
In this world we evidence an order of active cause. SummaEvery being has a cause in this changing world and this is the cause of another being. Fusus al-Hikam
Divine attributes:
Divine attributes:
God is an absolutely eternal Being. Summa God is an eternal Being without cause. Al-Siyasat al-Madaniyyah
Al-Farabi synthesizes Aristotelianism and Neo-Platonism but supports the trends towards Neo-Platonism in the medieval West. As E. Gilson has shown, al-Farabi's translations were long used as arguments by those Western philosophers who wished to reinstate the Augustinian era.
With al-Farabi originated the idea of definite determinism based on a metaphysical foundation. As a result this conception led to the distinction between psychological necessity and physical necessity. God is the Necessary Being according to al-Farabi (Wajib al-Wujud) and takes necessity from Himself. All other beings take their necessity from God. The conception of God understood as Universal and Necessary Being is substituted in this way for the conception of God as the “efficient autonom”
of the theologians.
The world which takes its necessity from God and is as necessary as God Himself depends no longer, as in Aristotle, on the subtle laws of beauty and habit. It is not dependent on the autonomous will of God either. Thus, physics found a stronger and more unshakable foundation in al-Farabi than in the Greeks. This foundation is the metaphysical conception of necessity.
During the era of translations into Latin, the following were the main translations from al-Farabi:
John of Seville and Gundisalvus,
Liber Alpharabii de Ortu Scientiarium.
Gerard of Cremona,
Liber Alfarabii de sillogismi, De Divisions, de Scientiis,
Distinctio super librum Aristotelis de naturali auditu
Liber Alf arabii de Scientiis.
Hermann the German,
Declaratio compendi viam divisions Alf arabii super libri rhetoricum Aristotelis ed f ormam clariorom et totale reducta.
To this list may be added E. Gilson's edition of De Intellectu et intellects with a French translation.
The philosophical development of the great Arab physicist ibn Haitham (Alhazen) proceeded from skepticism to a kind of criticism. The evolution from scepticism to his own ideological synthesis, he owed to al-Farabi. The Latin translations of some of ibn Haitham's books written during his empiricist and skeptical periods were instrumental to the development of Roger Bacon's ideas.
In addition to this, Western science profited by ibn Haitham's detailed research on optics. He really marks the beginning of physics as well as that of the movement of empiricism in the West. In the origination of empiricism, his role is even greater than that of al-Razi. Ibn Haiiham explained the role of induction in syllogism. He criticized Aristotle for the meagreness of his contribution to the method of induction which he regarded as superior to syllogism. He considered it to be the basic requirement for true scientific research.
Besides his analysis of light, ibn Haitham devoted the major part of hi book to a detailed discussion of the problem of perception. He studied the perception of darkness, distance, position, body, size, and then in the menta field, the perception of proportion, appearances, and beauty. He saw the relation between perception and reflection and showed great acuteness i explaining how true knowledge is founded on these two processes. He held that knowledge combines the substance of the intellect with the content o experience and, thus, reconciled rationalism with empiricism.
The influence of ibn Sina on the West was very significant. During the period of translations into Latin, many of his books became known in the West. His greatest work al-Shifa' was first transmitted to the West in th fifth/eleventh century through Yanbu'al-Hayat,a philosophical work by the Jewish philosopher, Solomon b. Gabriel (known to the Latins as Avencebrol o Aviceborn).
Many adaptations of ibn Sina's philosophy were made by the Latin philosophers. B. Haneberg has given an elaborate account of this influence (Zu Erkenntnislehre von ibn Sina and Albert us Magnus, 1866). In his article published in Arch. d'hist. et lit. du Moyen Age, Gilson shows this influence still more full) By comparing the Latin translations of ibn 8-ma's works with the origin, Arabic texts we have prepared the following table of parallel terminology.
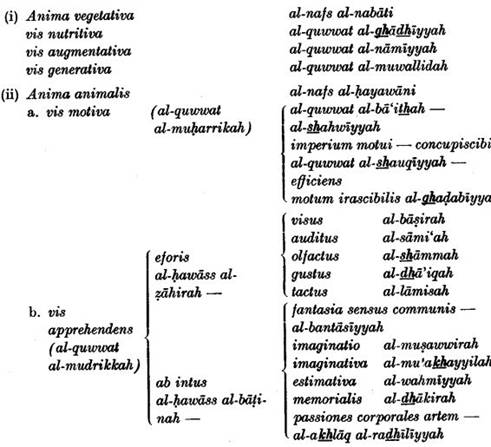

The translation movement received new impetus during the beginning of the sixth/twelfth century. By his work Daldat al-Ha'irin (The Guide for the Perplexed) Maimonides introduced Muslim philosophers and especially ibn Sina (Avicenna), to the West in great detail.
During the same century arguments started between Abelard and St. Thomas in the Latin world. Numerous translations from Arabic into Latin, especially of al-Farabi and ibn Sina, during that era suddenly widened the horizons of thought in the West.
During the sixth/twelfth and seventh/thirteenth centuries the main centres where translations were made from Arabic into Latin were Toledo, Durgos, Sicily, and Naples. Translations made by John of Seville and Gundisalvus were of primary importance. The first translated Arabic texts into the Roman language and the second, from Roman into Latin. Ibn Sina's al-Shifa was also partly rendered into Latin and entitled Suffacientia. Kitab al-Qanuln fi at-Tibb (Canons of Medicine) was also translated during the same period. The Latin rendering of the works of these as well as of other Muslim philosophers continued during the seventh/thirteenth century.
The influence of these translations has to be classified in two groups.
i) The influence beginning with ibn Sina and al-Farabi and leading to the development of the trend of Avicennism.
ii) The continued influence exercised by al-Ghazali's summaries of al-Farabi's and ibn Sina's views.
The translations from al-Farabi and ibn Sina helped in the establishment of Augustinian philosophy. It supplied it with affirmative arguments. Hippone, in his book Doctrine Sacra, succeeded in making that synthesis. Ibn Sine's influence on medieval Christian thinkers was of primary importance sincethey profited by his ideas directly and also since he was useful in interpreting St. Augustine. However, the Augustinians, who were adherents of ibn Sina and had accepted the major ideas of the Muslim philosopher, severely attacked some of his doctrines.
This trend originated from De Anima the authorship of which had been attributed to Gundisalvus for a long time though later on the probability of its belonging to John of Seville increased. This is a work fully inspired by ibn Sina. It was published in 914/1508 in Venice as a preface of Shifa'.
In the seventh/thirteenth century an effort was made at the reconciliation of St. Augustine's ideas with those of Aristotle-a reconciliation for which ibn Sina's system served as an appropriate basis. This led to the movement called Augustinian-Avicennism. William of Auvergne was the most important witness of Latin Avicennism.
His mentioning ibn Sina in different sections of his books forty times indicates how full he was of his ideas. William benefited from ibn Sina's definitions, his classification of the sciences, and many of his ideas on theology; used the examples he borrowed from him; and took over with some modifications his idea that “the celestial sphere is a living being”.
Carra de Vaux states that William's idea of the immortality of the soul-immortalitate anime-was inspired by ibn Sina. However, William attacked ibn Sina for such ideas as the eternity of the universe, the necessity of creation, and the separate active intellect taken as the efficient and final cause of all souls, etc.
It was for this reason that, according to the decrees issued in 607/ 1210 and 612/1215, the teaching of Aristotle's interpretations and, among them, ibn Sink's books were prohibited by the Church. While William was criticizing Aristotle and ibn Sina, there were other Western thinkers of his time who were benefiting from the great Muslim philosopher. In de Vaux's terms, they were not Avicennists reconciling ibn Sina, as William did, with Christianity, but Avicennists who followed him in all respects.
Many Christian philosophers during that era accepted ibn Sine's theory of knowledge instead of Aristotle's. We observe the highest development of this trend in favour of ibn Sina, especially in Roger Bacon's illuminism. According to de Vaux, he was an Avicennist. Among the renowned scholars of the seventh/thirteenth century, he was the one best informed about ibn Sine's life and works. He did not only know all of ibn Sine's works translated into Latin, but also knew that apart from these he had other books in Arabic. With ibn Sine's treatise “Oriental Philosophy,” now lost, he was well acquainted.
He not only knew his works on philosophy, but also those on astronomy, medicine, and alchemy, and since he was an empiricist, he benefited to a great extent from ibn Sina's researches and did not stick to the limited view of the scholastics concerning him. He even claimed to have found in him the doctrine of the Holy Ghost and that of the origination of the universe in time. According to Gilson, his thesis on illumination is connected with ibn Sina's idea of the separate active intellect.
Roger Bacon followed ibn Sina in social ethics, conception of the CityState, and also in philosophy of religion. He argued that God is eternal, and His being eternal signifies infinite power. Infinite power necessitates infinite quality and, therefore, infinite goodness and sagacity. If the power of the First Cause is infinite, then the universe can be created by it.
Goodness of the First Cause necessitates its creation by It and its sagacity necessitates its creation according to purpose. Ibn Sina had arrived at the same conclusions through the same kind of thinking (E. Gilson, “Les Sources, etc.,” Archives, 1930).Alfred of Sareshel also studied ibn Sina and, like Roger Bacon, was an Avicennist in a broad sense.
The book entitled De Causis Primis et Secundis was attributed to ibn Sina for some time, because the anonymous author of this work was throughout inspired by him. Without mentioning the name, he refers to ibn Sina's Metaphysics three times and to his De Anima once. In another place, without mentioning hiss name, he quotes passages from him. Many times he summarizes him or makes free adaptations from him. The plan of the book as well as the dominant topics belong to ibn Sina altogether.
In the book entitled De Division Naturae the author of which is also unknown, ibn S-ma's views are partially Christianized and St. Augustine's ideas are partially laicized in an attempt at reconciliation. Gilson regards this book as the limit of Augustinian-Avicennism. De Vaux sees an apparent Avicennism in it. The most daring passages from ibn Sina have been adopted in it without modifications. Ibn Sina dominates the book.
On the other hand, Erigena and St. Augustine are included in it with many modifications and further interpretations. In fact, texts from Erigene and Denys together with ibn Sina's cosmism are put into a Christian composition.
Eventually, the influence of Avicennism got stronger than Augustinianism. For instance, the classification of intellects by al-Farabi and ibn Sina dominated Albert the Great. St. Thomas was still under the influence of these philosophers even when he criticized them just as al-Chazali was under their influence on many points even when he offered a criticism of them.
Ibn Sina, was getting known in the Western world also through the efforts of John of Seville who is named Hispanensis in some of his translations. David, his father, was of Jewish origin after whom he is also called ibn Dawud. Some of ibn Sina's books on metaphysics were translated by him. John compiled these under the title Opera (Majmu'ah = Collections), and it was twice published in Venice, in 901/1495 and in 906/1500.
The following books have been included in this Opera:
1. Logika;
2. Suf ficientia;
3. De Coelo et Mundo;
4. De Anima;
5. De Animatibus;
6. Intelligentia (Kitab al-'Aql);
7. Philosophia Prima (Falsafat al-fla).
Ibn Sing's classification of the philosophical sciences was widely accepted in Europe in the Middle Ages and was preferred by the scholastics of the seventh/thirteenth century to that of any other. By his reading of ibn Bajjah's books, the Latin translations of most of which have now been lost, Albert the Great was led to the study of ibn Sing's works as also of al-Ghazali's.
Both he and his disciple Ulrich of Strassburg were influenced by him. The former followed ibn Bajjah's method and regarded him as the greatest commentator of Aristotle. One of the many new ideas that ibn Sina handed down to the West was that of intentio or the intelligible. His classification of the soul was also accepted by Albert the Great and through him by many medieval Western philosophers. One also sees ibn Sina's influence on St. Bonaventure and St. Thomas.
St. Thomas criticized ibn Sina indirectly while making a penetrating study of ibn Rushd (Averroes). In his book entitled Contra Averroistas, he examined all the interpretations of Aristotle made by ibn Rushd, and he profited by the ideas of Albert the Great who was his master. That way he got up to ibn Sina. St. Thomas developed his own philosophy by giving new meaning and direction to Aristotle while explaining and criticizing ibn S-ma's and ibn Ruahd's theories on the problem of the intelligible as separate from the material (al-mufariqat).
According to St. Thomas' explanations in this book, for ibn Sina all knowledge of the universal depends upon the knowledge of the particular, that is, the universal can be comprehended only with the help of the lower faculties, like perception, memory, and imagination. A totally naturalistic philosophy appears here, although the philosopher is altogether in the field of metaphysics.
According to ibn Sina, the deeper our soul gets in the field of sensations, the nearer does it get to the intelligibles. According to St. Thomas, however, the farther the soul gets from sensations, the closer does it get to the intelligibles. According to him, ibn Sina's doctrine is a form of Platonism without being faithful to it in its results.
It is certain that the translations of the majority of ibn Sing's books into Latin led to a considerable change in Western thinking. E. Gilson studied his influence on Duns Scotus in the article: “Avicenne et le point de depart de Duns Scotus,” Arch., 1927. Ibn Sina's views about the definition and classification of the soul had a wide influence. Ibn Sina defines the soul both as maturity of the body, entelechy, or form, as Aristotle had done, and as substance which is independent of matter.
This second definition marks the beginning of the conception of the soul as a substance independent of mattera conception which took its complete form in Descartes. The Muslim philosopher goes deep into the second category of the classification of the soul and, in order to prove that the soul is independent of the body, advances many arguments some of which, like the argument of identity and that of unity, were used by the Western philosophers following him.
The example of the flying man as cited by ibn Sina, in order to prove the substantiveness of the soul, given no doubt by the philosophers preceding him, was used in the West by St. Bonaventure and by others after him. Lastly, it may be noticed that ibn Sina's philosophy of illumination, developed under Neo-Platonic influence, paved the way for the development of several religiophilosophical trends in the West during the medieval period.
However, the failure to make complete translations of ibn Sina's works and to fill in the incomplete parts of Aristotle's texts found at a later date hindered the accurate appreciation of the Muslim philosopher and led even to the spread of certain vague ideas about him for centuries to come.
For ibn Sina as for al-Ghazali after him and for Kant in the modern age, the categories are subjective. Indeed, the Kantian position that the categories are subjective and the knowledge of objects is due to a synthesis of sense perception and logical intelligence, was a common place of Muslim philosophy in the sixth/twelfth century.
It was expounded not only by ibn Sina and al-G,hazali, but also by the latter's contemporaries: ibn Haitham, famous for his optics, and al-Birfini (d. 440/1048), well known for his studies in mathematics, astronomy, geography, and ethnology.
By the middle of the seventh/thirteenth century, almost all the works of ibn Rushd, known as Averro6s in the Latin world, had been translated into Latin. This translation work Was executed in various institutions by several scholars. At the college founded by Raymond, Archbishop of Toledo, some of the most important works of Muslim writers on philosophy and science, including Arabic versions of Aristotle and commentaries and abridgments by al-Farabi, ibn Sina, and ibn Rushd were translated into Latin.
One of the well-known translators working at Toledo was a German, Hermann by name, but his renderings of the Arabic translations of Aristotle's works were regarded by Roger Bacon as barbarous and unintelligible. Orientalists like Cassiri, Rossi, Jourdain erroneously regard ibn Rushd as Aristotle's first Arab translator.
In fact, ibn Rushd knew neither Greek nor Syriac, let alone his being the first translator of Aristotle. Aristotle's work had, in fact, been translated into Arabic and interpreted by many persons before him and ibn Rushd read him through these translations.
The following of ibn Rushd's works were translated into Latin and/or Hebrew: Tahafut at-Taha/ut (Destruction of Destruction) into Latin and Hebrew;
so was his Manahij al-Adilah, a work on philosophy and theology;
his Fasl al-Maqal which discusses the relationship between faith and philosophy was translated into Hebrew; the Latin version of his three volumes on Lav is entitled Vigilia super erroris reportas in textibus civilis.
There was also the Hebrew translation of ibn Rushd's summary of al-Majisti (Almagest) on astronomy, but only its Latin version is extant under the title De Motu sphearr celestis. His writings on medicine were compiled in a volume entitled Kulliyd (Compendium). These were translated into Latin and published in sever volumes entitled De Colliget.
Volumes 2, 4 and 7 were compiled by Jean Bruyerii Champier and entitled Collectanea de Remedica. He also wrote an interpretation of ibn Sina's poem on medicine entitled Urjuzah fi al-Tibb which was one of ibn Rushd's best known books. An epistle by ibn Rushd entitled Theriaque (Tirydq) too was translated into Latin and Hebrew.
Ibn Rushd's commentaries on Aristotle's works were translated into Latin by Michael Scot, Hermann the German, and others. Ernest Renan in his book entitled Averroi et l'averroisme gives full account of the Latin texts.
Ibn Rushd is considered to be the greatest interpreter of Aristotle in the Muslim world. He composed three kinds of works on the interpretation o' Aristotle, one in a summary form, another in medium size, and yet another in detail. But he was not an interpreter only; he was also an original thinker of no mean stature.
The trend he started in the West caller Averroism continued for centuries. Siger de Barbante was its last representative. Ibn Rushd considered all former interpretations of Aristotle t be deviations from the thought of the master. He tried to interpret his thought as it originally was, freed from all kinds of Neo-Platonic influences. It was through ibn Rushd's works that Aristotle became widely known in Europe. Those who were looking in the medieval period for the real Aristotle, and bad a glimpse of him from those preceding ibn Rushd, became enthusiastic Averroists.
No Muslim thinker influenced the medieval West more than ibn Rushd The main ideas for which he was vehemently opposed by the scholastics o the East and of the West and most enthusiastically welcomed by the radicals in thought from the sixth/twelfth to the eighth/fourteenth century an, which opened the door to the European Renaissance were : (1) allegories interpretation of the Scriptures, (2) the theory of two truths, which, in th, words of Macdonald, “ran like wild-fire through the schools of Europe,” (3) pan-psychism which implied immortality of the universal soul of humanity and mortality of the individual soul, (4) eternity and potentiality of matter, and (5) emancipation of women.
Ibn Rushd's theory of two truths, combined with the doctrine that matter is eternal and potent to produce all forms from within itself, was a godsend for the scientifically-minded people in the West who were, as a rule, condemned and persecuted by the orthodox Church and the State. They found in the above theses, which passed as Averroism, their best support. For this reason de Wulf calls ibn Rusted Doctor of the Anti-Scholastics.
In transmitting Muslim thought to the non-Muslim West, the Jews of Spain took the lead. During the short fanatical rule of the Berbers of Morocco, the Muwahbids, one of whom, abu Yusuf Ya`qub al-Mansnr (r.580/1184596/1199) banished even ibn Rushd from Morocco for a time to appease the orthodox, the Jews were persecuted and forced to migrate to the neighboring countries, viz., to Leon and Castile (the Christian part of Spain), to France across the Pyrehees, and to Sicily.
They were welcomed by Alfonso VI who had himself been educated among the Arabs and had done the work of initiating the Christians into Muslim thought. His successors Ferdinand II and Alfonso the Wise maintained the tradition and engaged Jewish scholars for translation work. Later, many of the Jewish scholars who were living in the country adjacent to the Pyrenees, having been turned out from there because of their Averroism, fled to other parts of Europe taking with them the learning of the Muslims.
Wherever they settled down they translated the works of Muslim thinkers, especially those of ibn Rushd whom they universally admired, from Arabic into Hebrew and from Hebrew into Latin. The family of Tibbonids established at Lunel undertook the translation almost exclusively of ibn Ruth--'s original works and his commentaries.
Such were Samuel ibn Tibbon's “The Opinions of the Philosophers,” Juda ben Solomon Cohen's “The Search for Wisdom,” and Gershon ben Solomon's “Gate of Heaven.” Among Jewish philosophers, while Ha-Levi followed al-Ghazali, and Maimonides ibn Sina, Gersonides was a disciple of ibn Rushd. Besides Jewish scholars, Jewish statesmen and travelers were instrumental in spreading Averroism in France, Italy, and Central Europe. The Friars also took a lead in accelerating the spread of Averroism; under their influence were translated Aristotle's works from the original Greek as well as ibn Rushd's commentaries on these works.
By the end of the sixth/twelfth century Averroism, i. e., the philosophy of ibn Rushd, had become so popular, particularly among the whole school of philosophers represented first by the Faculty of Arts at Paris, and had become such a menace to Orthodox Christianity that in 607/1210 the Council of Paris forbade all teachings of Aristotle's Natural History and ibn Rushd's commentaries on it.
This prohibition was confirmed by the Legate Robert of Courcon, Cardinal of Paris, in 612/1215, and renewed by the Popes in 629/1231 and 643/ 1245. The Physics and Metaphysics of Aristotle were forbidden at the University of Toulouse by Urban IV in 662/1263. In 668/1269 the Bishop of Paris condemned thirteen of ibn Rushd's basic doctrines, and in 676/1277 he condemned the prominent Averroist, Siger of Brabant. Yet the strength o Averroism was irresistible.
No force could suppress it. In 612/1215, Frederick II became the Emperor of Rome. Having bee] educated at Palermo under Arab teachers and having come into close contac with the Muslims of Sicily and during the Crusades also with those of Syria, h. had become a great admirer of Muslim thought in general, and of ibn Rush( in particular. In 621/1224 he established a university at Naples chiefly wit) the object of introducing Muslim philosophy and science to the people of the West.
St. Thomas received his education at this university. Here both Christian and Jewish translators were engaged for rendering Arabic works int. Latin and Hebrew. The works of Aristotle and ibn Rushd in their Latin translation were used not only in the curriculum of this university, but wer sent also to the Universities of Paris and Bologna.
Nowhere did Averroism strike deeper roots than in the Universities of Bologna and Padua. Of thess two centers of learning Padua became the “hot-bed of Averroism.”
Averroism became rapidly the ruling mode of thought in the West. Scholars of medieval Europe were agitated by ibn Rushd's Aristotle as by no other author. From the end of the sixth/twelfth to the end of the tenth/sixteenth century Averroism remained the dominant school of thought, and that inspite of the orthodox reaction it created first among the Muslims in Spar then among the Talmudists and, finally, among the Christian clergy. “His writings... after being purged of objectionable matter by ecclesiastic authorties became prescribed studies in the University of Paris and other institution of higher learning.”
Ibn Rushd became more famous in the Latin world than in the Mush world, because very few copies of his books had been made and circulated Muslim countries. Besides, the disgrace be had to face towards the end of 1 life was instrumental to his being forgotten. Another important reason f it was the destruction of his books in Spain by Ximenez's order. In pursuant of this order, 80,000 manuscripts in Arabic were burnt in the squares Granada.
In about 1009/1600, Scaliger, while searching for new manuscril in Spain, could find not even a single copy of ibn Rushd's works.
Philosophical Influence From Descartes To Kant
Although Pascal was a contemporary of Descartes, he cannot be said to have been a pioneer of modern philosophy in the West. Modern philosophical thought really began with the speculation of Descartes. Muslim philosophers had penetrated deep into the West much before Descartes' time, and most of the works of al-Ghazali had been translated into Latin before the middle of the sixth/twelfth century, and since then had exercised a considerable influence on Jewish and Christian scholasticism.
Much before Descartes, his skepticism had been taken up by Jehuda Ha-Levi (d. 540/1145) in his work Chosari and it had also shown its mark on Crescas (d. 813/1410). The Dominican Raymond Martin had freely used the Hebrew translation of Tahd/ut al-Falasifah, another of al-Qhazali's works, and incorporated a great deal of it in his Pugio Fidei. Pascal too had been deeply affected by his thoughts.
The influence that al- hhazali had on modern European thought has not so far been fully appreciated. There is no acknowledgment by Descartes of his indebtedness (direct or indirect) to any Muslim thinker, and yet it is difficult to believe that he did not know al-Ghazali's general position and was not influenced by it through the Latin scholastics, whom beyond question he must have read. This conclusion forces itself upon the mind all the more strongly when one realizes that he was not only a scholar of Latin, but had himself written two of his most important works, Meditationes de prima philosophia and Principia philosophiae, in Latin.
We notice that, exactly like al-Ghazali, Descartes came to his conclusions by a study of his own self, al-Ghazali's starting formula being “I will, therefore, I am,” and Descartes' being, “I think, therefore, I am.” He followed al-Ghazali's derivation of the negative and positive attributes of God from the concept of necessary existence.
The distinction made by him, and by Galileo before him, between the infinite (that the parts of which cannot be expressed by any number or measurement) and the indefinite (that which has no limit) was exactly the same as given by al-Ghazali and ibn Sina, and, following them, by Crescas and Bruno. Exactly like al-Ghazali he begins with describing how in vain he interrogated in his mind every school and every creed for an answer to the problems that disturbed him and finally resolved to discard all authority.
If the Muslim world had possessed the original of any mode of thought or movement, particularly in matters of detail, which was developed by the West later, when most of the classics of Muslim thought in the spheres of philosophy, medicine, and science had been translated into Latin, then, even in the absence of direct evidence, one would be justified in presuming that that mode of thought or movement was stimulated by influence from the Muslim East.
Although all other masterpieces of al-Ghazali had been translated into Latin before 545/1150, and had admittedly exerted great influence on the Western scholastic thought, there is no evidence that al-Ghazali's al-Munqidh min al-Dalal had been translated into Latin before Descarte's time.
It is for the scholars of Latin to discover that. But there is so much internal evidence in the most remarkable parallel of that work with Descartes' Discours de la methode, printed in 1047/1637, that it becomes impossible to deny its influence on the father of modern philosophy in the West.
Both of these works, al-Ghazali's al-Mungidh and Descartes' Discours de Influence of Muslim Thought on the West la methode, are autobiographical. Both al-Ghazali and Descartes began the stories of their lives from their youth (M. 4, D. 8).
Both realized how, despite having the same reasoning faculty, the children of Muslim or Christian parents, thanks to custom and example, had different beliefs from the beliefs held by those brought up by Jewish parents, and how those brought up among Frenchmen were different from those brought up among the Germans (M. 6, D. 19).
Both, therefore, decided that they would not believe anything that was based on tradition, custom, or example (M. 5-6, D. 13), and both walked into every dark spot to discover the truth (M. 4, D. 19). Both held, for exactly the same reasons, that the senses cannot yield certain knowledge (M. 8-9, D. 36).
The language and the examples of the defects of sense-experience given by both of them were almost identical (M. 8-9, D. 36, 37). Both studied all the literature that came into their hands, and in the accounts of their studies both mentioned the same subjects: philosophy, mathematics, logic, theology, and physical sciences. After examining all these subjects and all creeds one by one both concluded that they all fell short of certain knowledge and so resolved to discard all authority (M. 17-62, D. 8-14); and, thus, both became extremely skeptical about all that had passed as knowledge up to their times and boldly rejected the opinions they had so far held (M. 12, D. 17). Both of them, considering that the very same experiences as they had in waking life might occur also while they slept without there being at that time any truth in them, decided to feign that everything that had entered their minds till then was no more than illusion of dreams (M. 10, D. 31).
Both withdrew from their places of work, wandered in search of truth for several years from place to place (M. 3, D. 28), and finally went to lands quieter and more congenial for their search after truth (Tus and finally Nishapur in the case of one and Holland in the case of the other) (M. 3, D. 30). Both devised a new method of discovering the truth and this method was exactly the same for both. It consisted in taking only that as true which was conceived very clearly and very distinctly without any possibility of doubt (M. 5, 20, D. 20).
Both thought that the clarity and distinction they demanded of every truth must be at least that found in mathematics, that which we see, for example, in apprehending that 10 is greater than 3 or that the sum of the three angles of a triangle is equal to two right angles (M. 7, D. 35). Both modestly declared that the purpose of their discourses was not that everybody should follow their example, but only to relate the story of their own method of finding the truth; others may find the truth in some other ways (M. 19, D. 36f).
This most amazing resemblance between the two works makes George Henry Lewis say in his Biographical History of Philosophy that “had any translation of it existed in the days of Descartes, everyone would have cried out against the plagiarism.”
If it were only a few facts of their autobiographies, their going, for example, to quieter places for contemplation, and a few other things common to these works of al-Ghazali and Descartes, they might be considered to have been due to mere coincidence, but when the entire plan of their respective works, the whole treatment of the subjects discussed, and the whole content of these subjects down to detailed arguments, examples, and relatively unimportant matters, culminating in skepticism and in ultimate discovery of the method of finding the truth, run parallel to each other, it becomes impossible to attribute all that to coincidence.
It might be that along with other masterpieces of al-Ghazali, al-Munqidh too had been translated into Latin and read by Descartes. Nowhere has the existence of a translation of this work been mentioned, but nowhere has it been expressly denied. Alfred Guillaume in his article in The Legacy of Islam states, “His books on Logic, Metaphysics and Physics became known through the translators of Toledo in the sixth/twelfth century.”
He mentions no exception. It might have been one of the eighty-seven Arabic works translated by Gerard of Cremona or one of the works rendered into Latin by John of Seville and Dominic Gundisalvus. Or else it might have been the case that the text of al-Ghazali was orally translated for Descartes by some scholar of Arabic. Descartes himself refers to “the example of many fine intellects that had previously had this plan” (D. 29), but does not mention any by name. This may be a veiled reference to al-Ghazali who alone among his predecessors had followed exactly the same plan. In any- case, whatever the facts, in our opinion the influence of a1-Ghazali on Descartes' Discours de la mkthode is indubitable.
The next great luminary of modern philosophy was Spinoza. As shown by Dunnin Borkowski, he was deeply influenced by al-Farabi, whose ideas had reached him through Jewish scholars like Maimonides. “Any one who reads Spinoza's De Emendatione Intellectus would be struck by the great similarity between this book and al-Farabi's book What Should Precede the Study of Philosophy.
The succession of ideas in the two books is the same Even the final aim of the two books is the same, namely, the knowledge of God, `in order to follow His example as much as lies in human capacity.’”
Ibn Sina's influence on Spinoza through Maimonides is noticeable in his (Spinoza's) view that in God intelligence, intelligent, and intelligible are identical, and so are essence and existence, while in created beings existence is an accident super-added to essence.
As mentioned before, the cosmological proof for the existence of God given by al-Farabi and ibn Sins, was accepted by Spinoza, as by Maimonides and St. Thomas before him, and al-Ghazali's distinction between the infinite and the indefinite was followed by him as it was done by Crescas, Bruno, Galileo, and Descartes. Besides, his idea of substance was the same as al-Ghazali's idea of God-simple, having no accidental qualities, no distinction of genus and species and no separation of essence from existence.
His idea of freedom was also identical with al-Ghazali's idea of necessity (non-dependence upon anything else) and that of necessity was identical with the latter's idea of possibility (dependence upon a cause). Again, Spinoza's definition of the forms of imagination more or less conformed to the distinction between retentive memory and composite memory made by Maimonides following al-Ghazali In all these cases there is merely a difference of terminology.
The greatest name in modern philosophy after Spinoza is that of Leibniz But before we show his relation to Muslim thought, we should like to make a few remarks about the philosophy of another great thinker of the modern age, Kant, who claimed to be the Copernicus of philosophy.
Like al-Ghazali, Kant distinguished between phenomena and noumena and regarded the physical world of which alone the scientific knowledge is true as the world of phenomena, to which alone the categories, which to him are equally subjective, are applicable, causality, substance, and attribute bein; excepted by al-Ghazali. Like him, he demonstrates that theoretical reason cal analyse only what the senses yield, and that it cannot solve the basic and more important questions of philosophy and religion, such as the existence of God the nature of His attributes, the immortality of the soul, and the eternity c the universe. Kant found the key to the solution of these questions in the practical reason of man, while al-Ghazali discovered it in the religious experience of the Prophet and the mystic, which in its turn is to be tested by the moral certitude and moral influence which it exercises upon the soul. This comparison should make it clear as to who the Copernicus of philosophy was, al-Ghazali or Kant.
How are we to explain this close resemblance between the philosophic] ideas of al-Ghazali and Kant? We believe that this explanation can be foun in the philosophy of Leibniz, for, as T. H. Green observed, the doctrines Leibniz formed a permanent atmosphere of Kant's mind, despite the insp ration he received from Hume in his youth.
The minds of both worked o the same lines.
Kant was only a corrected and developed form of Leibniz, whereas Leibniz was an incorrect and undeveloped form of al-'Ghazali combine with the Asharite atomism.
Leibniz, like al-Ghazali and Kant, regarded the world as phenomenal. For him, as for these others, human knowledge does not consist solely in the perception of universal truths, nor does it entirely depend upon the sense Like both of them, he made a distinction between concepts and percept though he used different terms (relatively clear and confused perceptions) express this distinction.
Time and space for him, as for them, are not real characteristics of the real, though, like al-Ghazali and unlike Kant, he regards them not as intuitions but as ideas of relations. As for them, so for him, the categories-being, substance, unity, causality, identity, etc.-are supplied to experience not by the senses but by the mind.
Only their lists of these categories are in some details different.
Leibniz was a younger contemporary of Spinoza whose indebtedness to Muslim thought is undoubted. He could read Latin with the help of pictures at the age of eight; he wrote poetry in that language at the age of fourteen and read the scholastics during his youth. Therefore, he cannot be supposed to have been ignorant of al-Ghazali's views through Latin translations. In fact, the influence of Muslim thought on him is evident in some other respects as well.
Al-Farabi's proof of the existence of God from the concepts of necessity and contingency came down to him through ibn Sina, Maimonides, and St. Thomas, and his view that man's perfection comes from God and imperfection from his own nature is also traceable to Muslim scholastics. The same is true of his view of Goo as simple. Ibn Sina's influence on him can hardly be doubted for there is a curious parallelism in al-Shifa' and the Monadology of Leibniz in describing association and memory. The similarity is remarkable not only in the treatment of the subject but also in the example of the dog and the stick with which they illustrate their theory.
Without intensive research in the education that Locke and Berkeley received and the studies they pursued it is difficult to say whether al-Ghazali had any influence on their philosophy or not, but what we can say with certainty is that he anticipated much of their speculation. Like the empiricists from Locke to Hume, he bases knowledge on experience rather than on intellectual concepts, though he does not confine the meaning of the term “experience” to sensuous experience only, but extends it so as to include within it the intuitive experience of the Prophet, the mystic, and the saint, and thus escapes skepticism to which the European empirical thought inevitably led. This latter kind of experience is, according to him, far more important than sense-experience, since this alone yields the knowledge of Ultimate Reality.
Like Hume, al-Ghazali proclaims that we can have no knowledge of cause and effect in the realm of phenomena. All we know is that one event succeeds another. His description of induction is the same as Mill's. We perceive by the senses that the same thing repeatedly passes the same way (e.g., fire burns); we conclude that it will always pass the same way (fire will always burn); or we notice that certain things pass for the most part the same way (e.g., taking scammony is followed by diarrhoea or wine by intoxication); we judge that the one will probably follow the other in future cases as well.
But this explanation of induction is not based on the fallacy of petitio principii as Mill's. According to him, it is reason which judges that this sequence of events must come to pass by necessity, for if it came by mere chance could not have occurred always or in most cases in the past. It is, he sa3 by this argument alone that induction of empirical laws can be rational justified.
Al-Ghazali anticipates Schopenhauer and other voluntarists in holding that not thought but will is the fundamental reality, but he steers clear Schopenhatter's pessimism. God, according to him, is Will and the words flows from Him like a river. Like Bergson, even more like Jacobi and Schleik macher, he makes intuition or immediate consciousness the source of knowledge.
Al-Ghazali exerted great influence over the East and the West. It w the Protestant revolt that freed the West from the grip of this great mar intellect, and in the East, having conquered all rival thought; it has even this day a hold too tight to allow any fresh movement.
Philosophical Influence in the Post Kantian Period
In the sixth/twelfth century some stir was created by another Musl thinker ibn Tufail (Chapter XXVII) known in the Latin world for long Abentofal or Abubacer. Most of his writings were lost probably during the destruction by Ximenez. But his fame is due to his Hayy Ibn Yagzan, a philosophical romance, in which he shows that even without the help of tradition and revelation man can attain to the knowledge of nature and through that the knowledge of God.
This remarkable work was first translated into Hebre and Moses of Narbonne wrote an excellent interpretation of it. It was translat from Arabic into Latin by Edward Pococke Junior under the title Philo phus autodidactus sive Epistola Abi Jaafar ebn Tophail de Hai ebn Yokdh and published together with the Arabic text at Oxford in 1082/1671, and then its translations appeared in most of the European languages.
It was first translated into English by George Keith in 1085/1674, then by Geot Ashwell in 1098/1686. Simon Ockley published its translation into Engli from the original Arabic in 1120/1708. Its Dutch version was first publish in Amsterdam in 1083/1672 and again in 1113/1701. It was translated in German twice. Finally, Gauthier published the French version of the be with an analytic summary in 1318/1900. In Paul Bromilc's words, “in comparatively short time it caught the fancy of the public--in fact it to the world by storm and for a long time it remained in vogue.” The work interest in it has not yet ceased, for it was translated into Russian in 13. 1920, and into Spanish in 1353/1934.
The large number of these translations is indicative of the influence this philosophical novel on Western thought. After the appearance of translations, many books written in the West were inspired by this work. Among them may be Bacon's philosophical novel, Atlantis, and other Utopian novels, the last of which was Robinson Crusoe produced by Daniel Defoe in 1132/1719, eleven years after the publication of Simon Ockley's translation. It has, therefore, been justly concluded that, among others, Daniel Defoe was indebted to the great Muslim philosopher for the conception of his work.
In discussing the influence of Muslim philosophy on Western thought we cannot omit the reference to ibn Khald0n. He has been recognized by many to be the father of sociology and the first philosopher of history. He was the first to oppose Greek and early Muslim philosophers explicitly by asserting that human societies should not be studied from an idealist-rationalist point of view, but ought to be taken as natural phenomena.
This view is fully expounded in his Muqaddimah (Introduction) to his historical work entitled Kilab al-'Ibar. The Introduction was first printed in Paris by Quatremere and then by Mustafa Fehmi at Bfilaq. Its first translation was made in Turkey by Pirizade Sahib Molla and Ahmet Jevdet Pasha.
Western people were not aware of this philosopher until the beginning of the twelfth/eighteenth century. At the end of the eleventh/seventeenth century, d'Hiberbelot merely referred to him in Bibliotheca Orientalis; Sylvestre de Sacy emphasized his importance at the beginning of the thirteenth/nineteenth century.
At the end of that century, Hammer Prugstall wrote articles about him and referred to him as the “Montesquieu of the Arabs.” Some years later, Garcin de Quatremere published the original version of the “Introduction” under the title Prolegomenes d'Ebn Khaldoun and attempted a summarized translation of it but could not finish it. Baron de Slane succeeded in making a complete translation between 1279/1862 and 1285/1868. In 1351/1938 this translation was reproduced in photoprints.
This translation made it possible for philosophers and sociologists to study the text. In the West since then, ibn Khaldun has been often referred to by Western thinkers and some have considered him the founder of a new science. Some consider him a philosopher of history. Others think he pioneered sociology. For instance, Rappoport, R. Flint, N. Schmidt think he is a philosopher of history. Gumplowitz, R. Maunier, Findikoglu, Sati'u Bey al-Husri, and Schmidt consider him the pioneer of sociology.
According to Gaston Bouthoul, he had both these qualities. He regards him as the leader of the biological conception of society-a conception later worked out in their own way by Vico, Montesquieu, and Marx. F. Schulz wrote many articles on ibn Khaldun in the Journal Asiatique (Paris, 1303/1885). Graberg of Hemso, Franz Rosenthal, von Kremer, Lewine, G. Bouthoul, Gabrieli, Stefano Colosio, Ferreiro, Carra de Vaux, T. J. de Boer, G. Richter, Gauthier, A. Bombaci, Charles Issawi, W. Fischel, D. B. MacDonald, Breisig, H. A. R. Gibb, R. Altemira, etc., have referred to him since the end of the last century. As a result of this strong interest shown by the Orientalists in him, his conceptions of history and society have had an influence on some contemporary philosophers of history such as Spengler and Breisig.
Bibliography
Ibn al-Qifti, Tdrikh al-Hukama'; ibn abi Uyaibi'ah, 'Uyun al-Anbd' f Tabagat al-Atibba'; ibn al-Nadim, Fihrist; Bhahraetani, al-Milal w-al-Nilual; §hahraziui, Tarikh al-Hukama'; Baihaqi, Siwan al-Hikmah; M. Meyerhof, Von Alexandrien nach Baghdad, Cairo, 1930; A. Jourdain, Eecherches Critiques cur l'dge et l'origine des traductione latines d'Aristotle; F. Wiistenfeld, Die tlbersetzungen arabiseher Werke in das Lateinische seit dem XI. Jahrhundert, Gottingen, 1877; Die Akademien der Araber and ihre Lehrer, 1837; D. Campbell, Arabian Medicine and Its Influence on the Middle Ages, 1926; S. Munk, Melanges de philosophic juive et arabe, Paris, 1859; M. Steinschneider, Die europaischen Uberaetzungen aus dem Arabischen, his Mitte des 17. Jahrhunderts, 1904; Die hebrdischen Ubersetzungen des Mittelaltere, Berlin, 1893; Victor Chauvin, Bibliographic des ouvragea arabes ou relatif aux arabes, publics dans l'Europe Chrdtienne de 1810 A 1885, Liege, 1922;
J. Forget “Do l'influence do la philosophic arabe sur la philosophic scolastique,” Reuve Neo-Scolastique, Oct. 1894, pp. 385-410; A. Schmolders, Documenta philosophia arabum, Bonn, 1836; Essai our les ecoles philosophiques chez lea Arabes et notamment sur le doctrine d'Algazzali, Paris, 1942; M. Bouyges, Notes our lea philosophies arabes connus des latins au Moyen-Age, Beyrouth, 1922; A. F. Mehren, “Correspondance d'Ibn Seb'in avec Frederic II”, Journal Asiatique, Vol. XIV, 1879; Algazel, Magacid at-falasifat, cite par Saint Thomas sans Summum; Algazel, Taha f at al-Falasi f at, cite par Raymond Martini; C. Huit, Les Arabes et l'Aristotelisme, Bans les Annales de Phil. Chretienne, Vol. XX, Paris, 1890; Haneberg, Zur Erkenntnislehre von Ibn Sina and Albertus Magnus, 1868; S. Beitriige, Zur Psychologie de Ibn Sina, Mdnehen, 1872; G. Quadri, La Philosophic Arabe daps i'Europe MEdievale, des origins a Avexroestrad de b'italien, Paris, 1947;
E. Gilson, “L'auguatinisme avicennisant,” Archives d'Histoire doctrinale et littdraire du Moyen-Age, 1929; A. M. Goichon, La Philosophic de'Avicenne et son Influence en Europe medicvale, Paris, 1944; Ernest Renan, Averroes et l'averroisme, Paris; Calmant-Levy, L'lslam et 1'Occident, Melanges composes par plusieurs auteurs, Cahier du Sud, 1947; Leon Gauthier, Ibn Rochd (Averroes), Paris, 1848; Miguel Asin Palacios, Huellas des Islam, 1918, La spiritualidad de Algazely su sentido cristiano, 4 Vols., Madrid, 1934-941; Emile Brehier, Histoire de la Philosophic; H. Z. Ulken, Islam Medeniyetinde Tercumeler, Istanbul, 1947; La Penile de l'Islam, Istanbul, 1953; Islam Felsefeei Tarihi, I,1957; “Ibn Sins,” “Ibn Rughd “ Islam Ansiklopedisi, (Turkish; G. M. Wickens (Ed.), Avicenna, Scientist & Philosopher, Luzac, London, 1952.
Notes
 0%
0%
 Author: M.M. Sharif
Author: M.M. Sharif








